
ADVANCED PROJECTILE MOTION EQUATIONS FREE
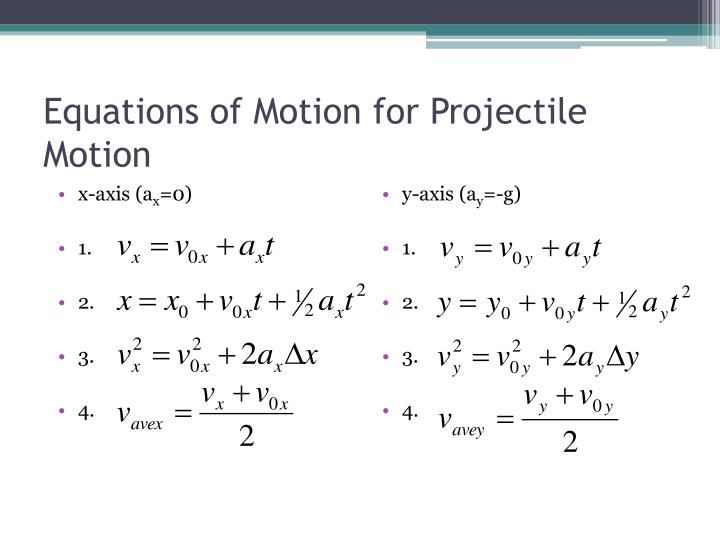
Once the strong> flight time is obtained, simply substitute in the equation of position of the horizontal component. Initial horizontal velocity is typically written as ux subscript x is used to represent the horizontal rectilinear motion. Equations of Motion and Free Fall In this lesson we practice using the equations of motion to solve projectile motion problems. It is the maximum horizontal distance, from the starting point of the motion to the point in which the body hits the ground. Use one-dimensional motion in perpendicular directions to analyze projectile motion. That is, the flight time is the time required for the height to become 0 (the projectile reaches the ground). It is calculated for y = 0, the vertical component of the position. From that time, and from the equations of position, we can calculate the distance to the origin in the both axes, the x-axis and y-axis. projectile motion by describing advanced theories of mechanics and. Starting from the equation of velocity in the y-axis, and making v y = 0, we get the time t that it takes the body in get to this height. derivations of differential equations for a horizontal shot, a vertical shot. The Physics Classroom demonstrates the process of analyzing and solving a problem in which a projectile is launched horizontally from an elevated position. This value is reached when the velocity in the y-axis, v y , is 0. On the other hand, frequently in exercises, you would be asked for some of the following values. an introduction to projectiles or at a more advanced level where calculation. On the other hand, to know which trajectory the body follows, that is, its equation of trajectory, we can combine the above equations to eliminate t, getting:Īs expected, this is the equation of a parabola. This episode looks at the independence of vertical and horizontal motion. For example, enter the time of flight, distance, and initial height, and watch it do all calculations for you!īe sure also to check the parabola calculator to learn more about such a curve from a mathematical point of view.The equation of position of the projectile motion is given by: Using our projectile motion calculator will surely save you a lot of time. Include: horizontal and vertical components of motion of the. V o is the initial velocity sin is the component along the y-axis cos is the component along the x-axis The formula of projectile motion is used to calculate the velocity, distance and time observed in the projectile motion of the object. Solve simple free-fall problems using the special equations for constant acceleration. The object moves with constant velocity in the. Equations related to the projectile motion is given as. Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y = h + V y 0 t − g t 2 / 2 y = h + V_\mathrm / (2 g) h max = h + V y0 2 / ( 2 g ) At t 0, the ball is released at the position specified by coordinates (0, y0) with horizontal velocity vx.Modern Physics :- This portion covers a lot of portion in JEE Advanced.



Horizontal distance traveled can be expressed as x = V x t x = V_\mathrm x t x = V x t where t t t is the time. For most problems do the vertical motion first and use the suvat equations.We tackled both problems in the horizontal projectile motion calculator and free fall calculator, respectively. If, additionally, α = 90°, then it's the case of free fall. If the vertical velocity component is equal to 0, then it's the case of horizontal projectile motion. Three vectors - V V V, V x V_\mathrm x V x and V y V_\mathrm y V y - form a right triangle.The vertical velocity component V y V_\mathrm y V y is equal to V sin α V \sin\alpha V sin α. A bag of mass 1000 g, projected at an angle of 90 from the ground with an initial velocity of 5 m/s, acceleration due to gravity is g 10 m/s2, what is the.The horizontal velocity component V x V_\mathrm x V x is equal to V cos α V \cos\alpha V cos α. Februby Mir Equations for the linear motion and free fall are known to all.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
